Introduction
Cities around the world are experiencing a digital transformation, and at the forefront of this revolution is urban lighting. No longer are street lights mere sources of illumination; they have evolved into sophisticated smart street light systems that integrate energy efficiency, connectivity, and intelligent control. This article examines the history and technological advancements behind smart street lights, detailing how these systems are reshaping urban safety, sustainability, and efficiency.
Throughout this discussion, the keyword smart street light remains central—underscoring every innovation, benefit, and future trend. As urban planners, municipalities, and technology enthusiasts seek reliable, energy-saving, and innovative lighting solutions, understanding the ins and outs of smart street lights is more important than ever. We will cover the evolution of street lighting, compare conventional systems with modern smart street light technology, explore the components that make these systems work, and examine their economic, environmental, and urban-planning impacts. In doing so, we will also highlight LEOTEK’s role as a leader in smart street light technology, particularly through its innovative smart node for lighting control.
1. The Evolution of Street Lighting: From Conventional to Smart Street Light Systems
1.1 A Historical Perspective
The journey from basic public illumination to today’s high-tech smart street lights is a story of human ingenuity and technological progress.
- Ancient Beginnings:
Early civilizations used torches and oil lamps to light streets and public spaces. Although rudimentary, these light sources laid the groundwork for public illumination. Over time, the idea of a smart street light—one that could do more than simply provide light—was born out of necessity for safer and more reliable urban spaces. - The Gas Lighting Era:
In medieval and early modern cities such as London, gas lanterns began to replace oil lamps. By the early 19th century, gas street lighting became widespread in urban centers like Baltimore and Paris, marking the first organized approach to public lighting. However, these systems were static and did not adapt to changing conditions—a stark contrast to today’s dynamic smart street light systems. - The Electrical Revolution:
The advent of electricity brought dramatic change. Electric street lights replaced gas lamps in the late 1800s, with early experiments using arc lamps and incandescent bulbs. Thomas Edison’s invention of the carbon filament incandescent lamp in 1879 paved the way for modern urban lighting, setting the stage for the future development of smart street lights. - The LED Transformation:
In the mid-20th century, the development of Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) revolutionized street lighting. LEDs offered improved energy efficiency, longer lifespans, and superior light quality compared to incandescent and fluorescent bulbs. Today, smart street lights predominantly use LED technology as their core, enabling enhanced performance and adaptability.
1.2 From Conventional to Smart Street Light Systems
While conventional street lighting systems were designed solely for static illumination, modern smart street lights incorporate a host of advanced features:
- Dynamic Illumination:
Smart street lights adjust their brightness dynamically based on real-time conditions. For example, a smart street light system can automatically brighten when it detects pedestrian or vehicular movement, and dim during periods of low activity. This adaptability not only conserves energy but also improves safety. - Integrated Sensors and Connectivity:
Unlike traditional street lights, modern smart street lights include sensors that detect ambient light, motion, and even environmental conditions. These sensors feed data into a centralized management system, enabling real-time adjustments and predictive maintenance. - Remote Management:
One of the most significant benefits of smart street light systems is their ability to be managed remotely. With technologies like wireless communication and IoT integration, municipal authorities can monitor and control street lights from centralized hubs—ensuring that every smart street light operates optimally. - Sustainability and Cost Savings:
The combination of energy-efficient LEDs and intelligent controls leads to significant reductions in energy consumption and operational costs. Over time, smart street lights prove to be far more cost-effective than conventional systems, while also contributing to a lower carbon footprint.
These advancements underscore the transformation from conventional lighting to smart street light systems—a transformation that is revolutionizing urban environments.
2. Components of Modern Smart Street Light Systems
Modern smart street light systems are complex networks that integrate various technologies to deliver superior performance and functionality. Below, we examine the core components that make up a smart street light system.
2.1 LED Fixtures
At the heart of any smart street light is its LED fixture. LEDs provide bright, clear illumination while consuming significantly less energy than traditional light sources. The use of LED technology is a cornerstone of modern smart street light systems, offering longevity, durability, and improved efficiency.
2.2 Luminaires and Structural Elements
Luminaires are the protective housings that enclose LED modules. These are designed not only for optimal light distribution but also to withstand harsh weather conditions. In smart street light systems, luminaires are engineered with aesthetics in mind—integrating seamlessly into urban landscapes while delivering superior performance.
2.3 Sensors and Detectors
Smart street lights are equipped with a variety of sensors that enable them to operate intelligently. Common sensors include:
- Motion Detectors:
Detect movement from pedestrians or vehicles, triggering the smart street light to adjust its brightness accordingly. - Ambient Light Sensors:
Monitor natural light levels to determine the appropriate intensity for artificial illumination. - Environmental Sensors:
Measure temperature, humidity, and air quality, providing data that can be used for broader urban management applications.
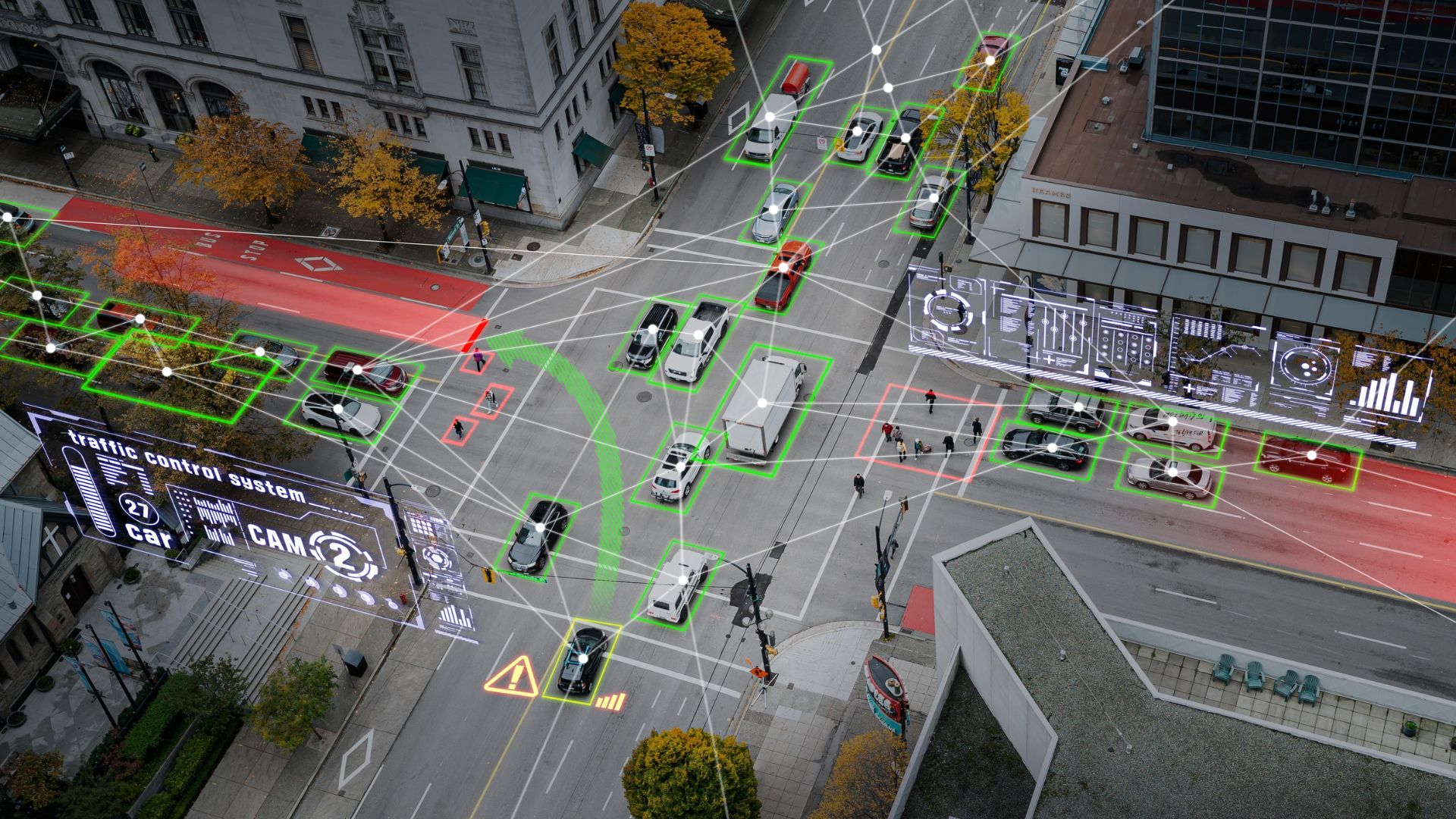
These sensors are critical for the adaptive functionality of a smart street light, ensuring that illumination levels are optimized for both safety and energy efficiency.
2.4 Control Systems and Communication Modules
The control system is the brain of a smart street light. It collects data from sensors and makes real-time decisions about light output. Communication modules—using technologies such as Zigbee, Wi-Fi, or 5G—allow these systems to transmit data to centralized management platforms. This connectivity is essential for remote control and maintenance, making it possible to adjust settings and diagnose issues without the need for on-site intervention.
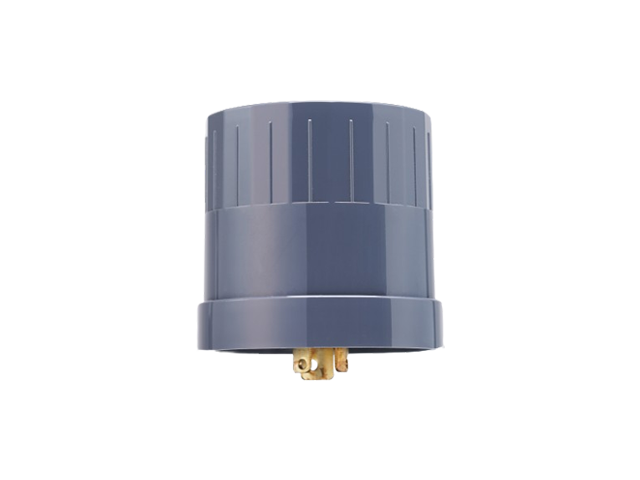
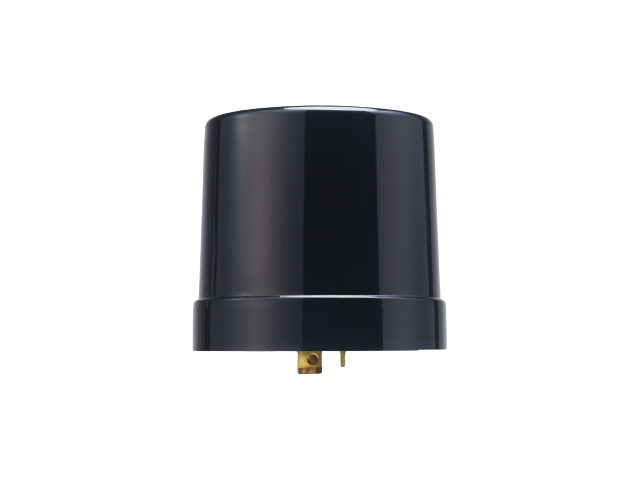
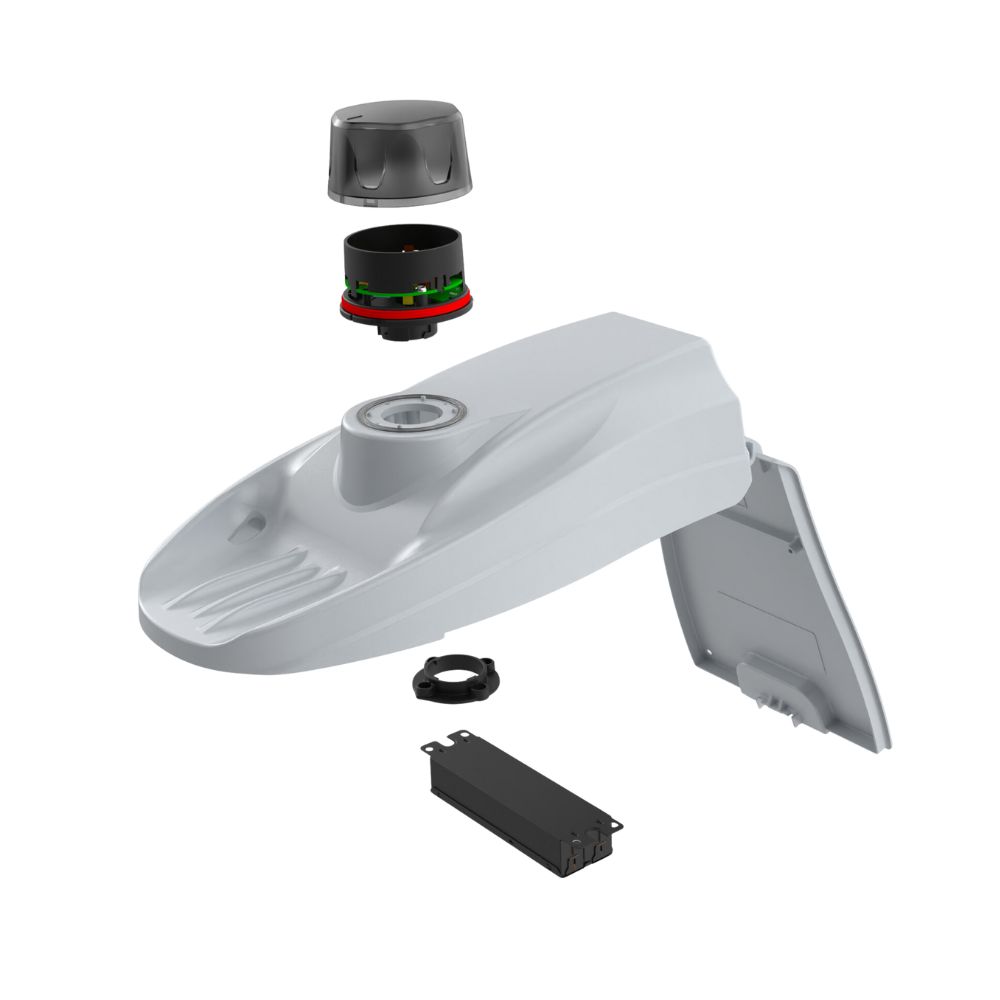
2.5 Smart Nodes and IoT Gateways
A critical advancement in smart street light technology is the integration of IoT-enabled smart nodes. LEOTEK’s smart node for lighting control is a prime example of how smart street light systems can be enhanced. These smart nodes act as intermediaries between individual street lights and the central control system, facilitating seamless data transmission and remote management. This connectivity not only improves system responsiveness but also ensures scalability as urban infrastructures expand.


3. The Benefits of Smart Street Light Systems
The shift from conventional street lighting to smart street light systems brings a host of benefits that extend far beyond mere energy savings. Below, we explore the various advantages offered by smart street lights.
3.1 Energy Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of smart street lights is their energy efficiency. Key factors include:
- Adaptive Brightness Control:
Smart street lights adjust their brightness based on real-time needs. During periods of low activity, the lights can dim, thereby reducing energy consumption. - LED Technology:
The energy efficiency of LED technology means that smart street lights require less power while delivering high-quality illumination. - Scheduled Operation:
Intelligent control systems can schedule street light operation to match peak demand periods, further optimizing energy use and reducing waste.
These factors combine to produce energy savings that result in lower utility bills and a reduced environmental impact.
3.2 Improved Public Safety
Smart street light systems enhance public safety in several ways:
- Enhanced Illumination:
By dynamically adjusting brightness, smart street lights ensure that urban areas are well lit when needed, reducing the risk of accidents and crime. - Integrated Surveillance:
Some smart street light systems integrate with security cameras and emergency response systems, providing additional layers of public safety. - Real-Time Monitoring:
Remote management and self-diagnostic features ensure that any malfunctioning smart street light is quickly repaired, maintaining consistent illumination across urban areas.
These features contribute to safer streets, making smart street light systems an essential element of modern urban security.
3.3 Environmental Sustainability
Smart street light systems offer significant environmental benefits:
- Lower Carbon Emissions:
Energy-efficient smart street lights reduce overall power consumption, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions. - Minimized Light Pollution:
Adaptive control systems help to limit excessive illumination, reducing light pollution and its impact on local ecosystems. - Support for Renewable Energy:
Smart street light systems are often designed to integrate with renewable energy sources such as solar power, further enhancing their sustainability profile.
By reducing energy use and supporting renewable resources, smart street lights help cities achieve their sustainability goals.
3.4 Economic Advantages
While the initial investment in smart street light systems may be higher than that for conventional systems, the long-term economic benefits are considerable:
- Reduced Operational Costs:
Lower energy consumption and reduced maintenance needs lead to significant cost savings over time. - Extended Lifespan:
The durability of LED technology means that smart street lights have a longer lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacements. - Enhanced Return on Investment (ROI):
Over time, the cumulative savings from reduced energy and maintenance costs offset the initial expenses, resulting in a positive ROI for municipalities.
These economic advantages make smart street light systems an attractive investment for urban infrastructure projects.
4. Integrating IoT and Connectivity in Smart Street Light Systems
The Internet of Things (IoT) has been a game changer for urban infrastructure, and smart street light systems are a prime example of IoT-enabled innovation. By connecting smart street lights into a unified network, cities can reap a variety of benefits.
4.1 Real-Time Data Collection and Analysis
Smart street lights are equipped with sensors that continuously collect data on environmental conditions, traffic flow, and usage patterns. This data is transmitted via wireless networks to central management systems. The ability to analyze data in real time allows urban managers to optimize street light performance and energy usage. Every smart street light in the network contributes valuable information, helping to refine control strategies and maintenance schedules.
4.2 Remote Monitoring and Control
Thanks to advanced communication modules, smart street light systems can be monitored and controlled remotely. Centralized management platforms provide a dashboard that displays the status of every smart street light in the network. Any issues, such as malfunctioning units or connectivity problems, are flagged immediately, ensuring rapid response times. This level of remote control is a key differentiator between conventional street lights and modern smart street light systems.
4.3 Predictive Maintenance
One of the most significant advantages of smart street light systems is predictive maintenance. By analyzing data collected from sensors, these systems can predict when a smart street light is likely to fail, allowing maintenance teams to address issues before they become critical. This proactive approach reduces downtime, extends the lifespan of smart street lights, and lowers overall maintenance costs.

4.4 LEOTEK’s Role in IoT Integration
A standout example of IoT integration in smart street light systems is LEOTEK’s smart node for lighting control. This device acts as an IoT gateway, connecting individual smart street lights to a central management platform. It enables real-time data collection, remote control, and predictive maintenance, making it an indispensable tool for cities looking to upgrade their street lighting infrastructure. LEOTEK’s smart node exemplifies how innovation in the smart street light space can drive urban transformation.
5. Comparing Conventional and Smart Street Light Systems
Understanding the differences between conventional street lighting systems and smart street light systems is critical for urban planners and decision-makers.
5.1 Conventional Street Lighting Systems
Traditional street lighting systems are characterized by:
- Fixed Illumination Levels:
Conventional street lights operate at a constant brightness, regardless of actual need. This results in excessive energy consumption and wasted power. - Manual Maintenance:
Maintenance for conventional street lights is typically scheduled at fixed intervals, without real-time monitoring or predictive capabilities. This reactive approach often leads to prolonged downtime and higher maintenance costs. - Limited Functionality:
Conventional street lights are designed solely to provide illumination. They do not incorporate sensors, connectivity, or other smart features that could enhance their performance.
5.2 Smart Street Light Systems
In contrast, smart street light systems offer:
- Adaptive Brightness Control:
Smart street lights continuously adjust their brightness based on real-time data. This adaptive feature ensures optimal illumination while minimizing energy usage. - Remote and Automated Management:
With integrated IoT connectivity, smart street lights can be monitored and controlled remotely. Automated diagnostics and predictive maintenance help reduce downtime and maintenance costs. - Enhanced Functionality:
Beyond illumination, smart street light systems can collect data on environmental conditions, integrate with security systems, and contribute to broader urban management initiatives. - Long-Term Cost Savings:
Although the initial costs are higher, the energy savings and reduced maintenance expenses of smart street light systems make them a cost-effective choice over time.
Clearly, when evaluating LED street lights vs. conventional options, smart street light systems offer significant advantages in energy efficiency, safety, and functionality.
6. The Role of Smart Street Light Systems in Urban Planning
Smart street light systems are more than just a lighting upgrade—they are an integral part of modern urban planning. By providing reliable data and adaptable performance, smart street lights help cities become safer, more sustainable, and more responsive to the needs of their residents.
6.1 Enhancing Public Safety and Security
Smart street light systems contribute to urban safety by:
- Improving Visibility:
With adaptive brightness and rapid response to pedestrian movement, smart street lights ensure that urban environments remain well lit during peak hours. - Supporting Surveillance Systems:
Integrated with security cameras and sensors, smart street lights can provide real-time surveillance data, aiding in crime prevention and emergency response. - Enabling Real-Time Monitoring:
The ability to monitor each smart street light remotely ensures that any issues are quickly resolved, maintaining continuous, high-quality illumination in critical areas.
6.2 Data-Driven Urban Management
Smart street light systems generate vast amounts of data that can be used to:
- Optimize Traffic Flow:
Data from smart street lights can inform traffic management systems, leading to smoother traffic flow and reduced congestion. - Improve Resource Allocation:
Municipalities can use data insights to prioritize maintenance, plan for future infrastructure developments, and optimize energy consumption. - Support Sustainable Urban Development:
The efficiency gains from smart street light systems contribute to broader sustainability initiatives, reducing the overall environmental impact of urban areas.
6.3 Economic and Social Benefits
Smart street light systems can also drive economic growth by:
- Reducing Operational Costs:
Energy savings and lower maintenance expenses free up municipal budgets for other infrastructure projects. - Enhancing Quality of Life:
Safer, better-lit urban environments contribute to improved quality of life for residents, potentially increasing property values and attracting new businesses. - Fostering Innovation:
The integration of smart technologies encourages further innovation, helping cities to become testbeds for new technologies and ideas.
7. Future Trends in Smart Street Light Technology
As urban areas continue to expand and evolve, the future of smart street light systems looks increasingly promising. Here are some key trends to watch:
7.1 Enhanced Connectivity with 5G
The rollout of 5G networks is set to revolutionize smart street light systems by providing faster, more reliable connectivity. With 5G, smart street lights will be able to transmit data more quickly, support higher-resolution sensors, and integrate more seamlessly with other urban technologies.
7.2 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The integration of AI and machine learning into smart street light systems will enable predictive maintenance, dynamic energy optimization, and improved response to changing urban conditions. These technologies will allow each smart street light to learn from historical data and adjust its performance for maximum efficiency.
7.3 Expanded Sensor Capabilities
Future smart street lights will incorporate an even wider range of sensors to monitor everything from air quality to noise levels. This expanded sensor suite will enable more comprehensive urban management, turning each smart street light into a mini environmental monitoring station.
7.4 Integration with Renewable Energy
There is a growing trend toward integrating smart street light systems with renewable energy sources such as solar panels. This not only enhances the sustainability of the system but also allows cities to become less dependent on traditional power grids.
7.5 Seamless Integration into Smart City Ecosystems
The evolution of smart street light systems will continue to drive the integration of urban infrastructure. As smart street lights become key nodes in the IoT network, they will interface seamlessly with traffic management, public safety, and environmental monitoring systems, creating a unified, data-driven smart city.

8. Implementing a Smart Street Light System: Strategies and Best Practices
For cities and municipalities considering the transition to smart street light systems, careful planning and execution are critical. The following strategies can help ensure a successful implementation:
8.1 Conducting a Comprehensive Needs Assessment
- Data Collection:
Analyze current lighting performance, traffic patterns, and energy usage to identify areas that would benefit most from a smart street light upgrade. - Stakeholder Engagement:
Collaborate with community leaders, urban planners, and residents to determine specific needs and expectations.
8.2 Phased Deployment and Integration
- Pilot Programs:
Start with pilot projects in select urban areas to evaluate performance and make necessary adjustments before a full-scale rollout. - Retrofitting Options:
For cities with existing conventional street lights, consider retrofitting with smart sensors and communication modules to gradually transition to a fully smart street light system.
8.3 Ensuring Scalability and Interoperability
- Modular Design:
Choose smart street light systems that are designed to scale easily and integrate with other smart city components. - Open Standards:
Adhere to industry standards for connectivity and data exchange to ensure that your smart street light system can evolve alongside other urban technologies.
8.4 Focusing on Sustainability and Cost Efficiency
- Energy Audits and ROI Analysis:
Regularly assess energy savings and maintenance costs to ensure that the smart street light system continues to deliver a strong return on investment. - Public-Private Partnerships:
Engage with technology partners—such as LEOTEK—to leverage expertise and share the financial risks of implementing cutting-edge smart street light systems.
9. Case Studies and Research on Smart Street Light Implementations
Numerous cities worldwide have already reaped the benefits of smart street light systems. A few notable examples include:
9.1 Case Study: Urban Renewal with Smart Street Light Technology
A mid-sized U.S. city replaced over 1,000 conventional street lights with smart street lights integrated with IoT sensors and adaptive controls. The results included:
- A 40% reduction in energy consumption.
- A significant decline in nighttime accidents due to improved visibility.
- A 30% decrease in maintenance calls thanks to predictive maintenance features.
This case study demonstrates the transformative potential of smart street light systems for urban safety, efficiency, and sustainability.
9.2 Research Findings
Recent research has consistently shown that smart street light systems offer:
- Lower Carbon Footprints:
Reduced energy consumption directly translates to lower greenhouse gas emissions. - Economic Benefits:
Long-term cost savings through energy efficiency and reduced maintenance expenses. - Enhanced Urban Mobility:
Integration with traffic management systems leads to smoother traffic flows and improved urban mobility.
The data reinforces the conclusion that investing in smart street light systems is not only an environmental imperative but also a sound economic decision.
10. Challenges and Future Directions for Smart Street Light Systems
While the benefits of smart street light systems are clear, there are challenges that must be addressed for widespread adoption.
10.1 Technical and Infrastructure Challenges
- Integration with Legacy Systems:
Upgrading existing conventional street lights to a fully smart street light system can be complex and costly. - Data Security and Privacy:
With increased connectivity comes the risk of cyber-attacks. Robust security measures must be implemented to safeguard the network of smart street lights.
10.2 Regulatory and Policy Considerations
- Standardization:
Establishing industry-wide standards is critical for ensuring interoperability and protecting user data. - Funding and Incentives:
Municipalities may require financial incentives or public–private partnerships to offset the initial costs of deploying smart street light systems.
10.3 Future Research Directions
- Advanced AI Integration:
Further research into AI-driven predictive maintenance and adaptive control could enhance the performance of smart street lights. - Renewable Energy Integration:
Ongoing studies on the integration of solar and wind energy with smart street light systems will be crucial for creating sustainable urban lighting solutions. - User-Centered Design:
Future smart street light systems should focus on user experience, ensuring that the technology not only meets technical requirements but also contributes positively to the quality of urban life.
11. Conclusion and Call-to-Action
The evolution of urban lighting from traditional systems to advanced smart street light systems marks a pivotal turning point for cities worldwide. Smart street lights have emerged as essential components of modern urban infrastructure—enhancing public safety, driving energy efficiency, and contributing to a sustainable future.
By integrating adaptive brightness, IoT connectivity, and advanced control mechanisms, smart street lights offer benefits that go far beyond conventional illumination. They enable data-driven decision-making, support dynamic urban management, and provide significant long-term economic and environmental advantages.
LEOTEK is proud to be a leader in this transformation. With decades of expertise in smart street light technology and innovative products like the smart node for lighting control, LEOTEK delivers state-of-the-art solutions designed for the evolving needs of modern cities.
Are you ready to revolutionize your urban landscape with cutting-edge smart street light solutions?
Visit LEOTEK Smart Node today to explore our full range of smart street light products and discover how our innovative technology can help transform your city into a smarter, safer, and more sustainable urban environment.
References
- TechTarget. (n.d.). What is a smart streetlight? Retrieved from https://techtarget.com/iotagenda/definition/smart-streetlight
- Verizon Business. (n.d.). How smart street lights can deter crime and improve safety in cities. Retrieved from https://verizon.com/business/resources/articles/s/how-smart-street-lights-can-help-deter-crime-and-improve-safety-in-cities/
- Itron. (n.d.). Intelligent streetlights | Smart cities. Retrieved from https://itron.com/na/solutions/what-we-enable/smart-cities/intelligent-streetlights
- Global Lighting Forum. (n.d.). Top smart street lighting companies. Retrieved from https://shine.lighting/threads/top-smart-street-lighting-companies.56/
- Sensus. (n.d.). Smart street lighting. Retrieved from https://sensus.com/smart-utility-network/smart-lighting/
- DC Smart Street Lights. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://streetlights.dc.gov/
- AEC Illuminazione. (n.d.). Smart street lighting systems | Smart city lighting. Retrieved from https://aecilluminazione.com/smart-street-lighting-system/
- New York Power Authority. (n.d.). Smart street lighting NY. Retrieved from https://nypa.gov/services/clean-energy-solutions/smart-street-lighting-ny
- Verizon. (n.d.). Intelligent lighting: Smart street lighting. Retrieved from https://verizon.com/business/products/internet-of-things/connected-smart-cities-communities/intelligent-lighting/
- Cities Today. (n.d.). The rise of super smart streetlights. Retrieved from https://cities-today.com/the-rise-of-super-smart-streetlights/